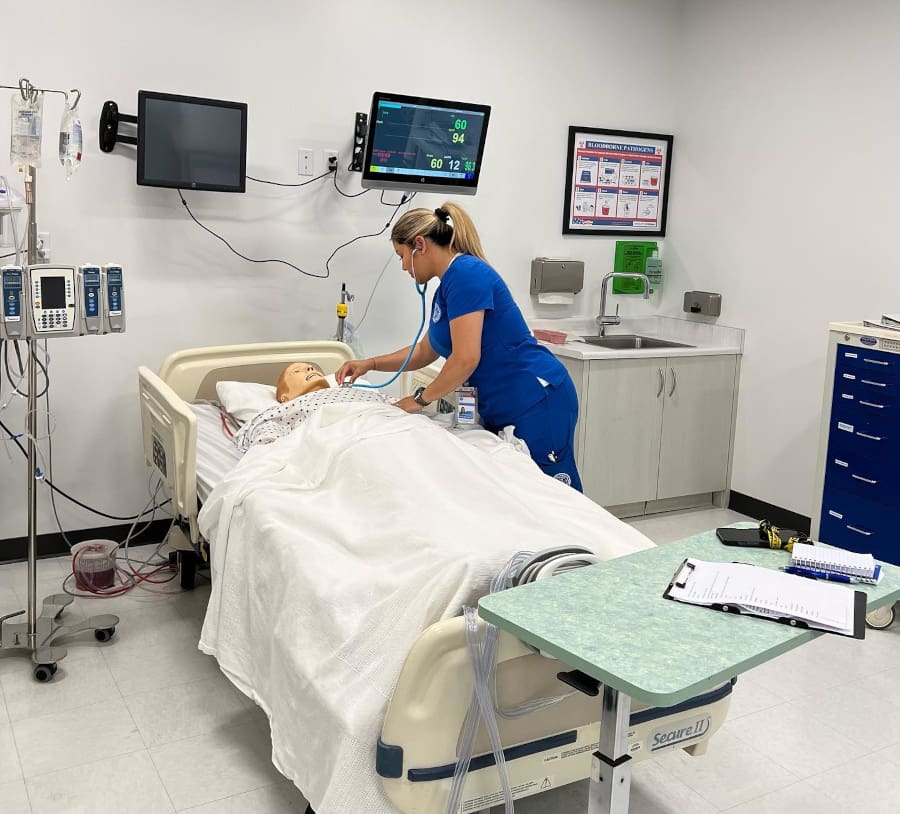
In recent years, healthcare simulation has become an essential component of nursing education, bridging the gap between classroom theory and real-world clinical practice. Harnessing advanced simulation technology enables nursing programs to ensure students gain practical, hands-on experience in a safe, controlled environment before entering the healthcare field.
The Importance of Simulation in Nursing Education
Healthcare simulation provides nursing students with opportunities to practice critical clinical skills without the immediate pressures and risks associated with real-life medical settings. This approach not only enhances the students’ clinical competencies but also boosts their confidence, critical thinking abilities, and decision-making skills. Through realistic scenarios, students learn how to handle complex patient interactions, medical emergencies, and routine care tasks, thus preparing them to manage real-world challenges effectively.
Types of Simulation Technology in Nursing Education
Simulation technologies vary widely, each offering distinct advantages for learning different skills and concepts. Here are some key examples of a few of these technologies.
High-Fidelity Mannequins
One of the most widely utilized simulation technologies in nursing education is the high-fidelity mannequin. These mannequins replicate real-life physiological responses, enabling students to experience authentic patient interactions. For instance, mannequins can simulate breathing, exhibit heart sounds, respond to medication administration, and even mimic medical conditions such as cardiac arrest, seizures, or anaphylactic reactions.
Nursing students engage with these sophisticated mannequins to practice essential clinical skills such as administering injections, performing CPR, and managing airway obstructions. This hands-on experience is invaluable, ensuring students are well-prepared to act swiftly and confidently in real-life medical emergencies.
Virtual Reality (VR) Simulation
Virtual Reality technology has emerged as a transformative tool in nursing education, allowing students to immerse themselves in highly realistic virtual clinical environments. Through VR headsets, students can virtually enter emergency rooms, surgical suites, or patient wards, interacting with virtual patients and medical equipment.
Using VR, students practice critical thinking, quick decision-making, and effective communication skills. For example, students might participate in a virtual scenario involving a mass casualty event, where they must prioritize patient care, triage effectively, and communicate clearly with virtual colleagues. This experience closely mimics the intense, high-stakes environment of a real hospital, preparing students for scenarios they may encounter in their professional nursing careers.
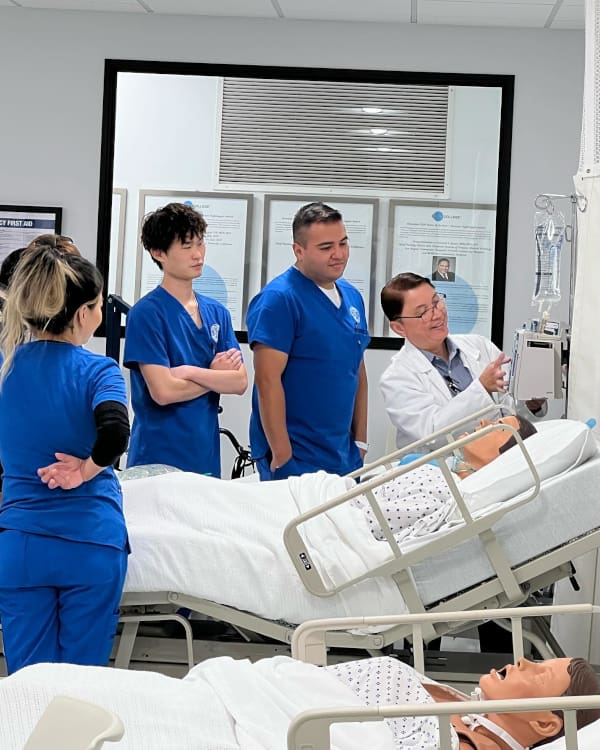
Digital Anatomy and Physiology
As technology continues to transform healthcare education, one of the most innovative tools making its way into the classroom and simulation lab is the 3D digital anatomy table. These life-size, interactive tables allow students to virtually examine and dissect detailed anatomical structures layer by layer, from muscles and organs to vascular and nervous systems. At institutions like CNI College, where immersive, hands-on learning is a core part of training, tools like this digital anatomy table play a crucial role in helping students build a strong foundational understanding of human anatomy. By engaging with realistic, full-body renderings, students can enhance their comprehension and better prepare for real-world clinical simulation scenarios.
Task Trainers
Task trainers are specialized simulation devices designed to teach and practice specific clinical skills. These may include models for intravenous (IV) insertion, catheter placement, wound care, or suturing techniques. Unlike comprehensive simulation scenarios, task trainers allow focused, repetitive practice on individual skills until proficiency is achieved.
For instance, as part of many degree programs, nursing students frequently utilize IV insertion task trainers. These trainers provide realistic feedback, enabling students to practice vein location, proper needle insertion, and securement of IV lines confidently and competently. Mastery of such skills in a controlled environment significantly reduces patient discomfort and improves safety when students transition to clinical practice.
Real-World Application of Simulation Experiences
The ultimate goal of healthcare simulation is to equip students with the skills, confidence, and judgment necessary to provide exceptional patient care. Simulation curriculum generally includes opportunities for focused skill reinforcement and remediation. This ensures that all students, regardless of prior experience, feel confident and competent before engaging with real patients. Real-world applications of simulation experiences include:
Improved Clinical Decision-Making
Simulated scenarios, such as managing cardiac emergencies or handling acute allergic reactions, teach students to quickly assess patients, recognize critical signs, and implement appropriate interventions. These experiences enhance the students’ ability to think critically and respond effectively under pressure, directly translating into improved patient outcomes in clinical practice. Structured debriefing sessions following simulation exercises are important to encourage students to reflect on their performance, discuss clinical decision-making, and receive personalized feedback. This reflective process reinforces learning and supports continuous improvement.
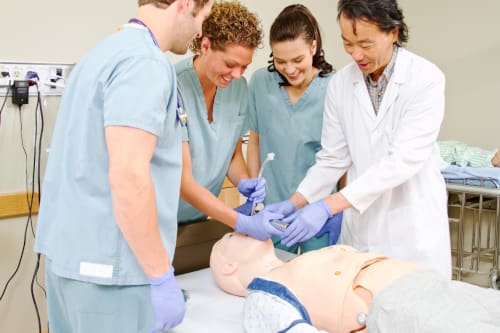
Enhanced Communication and Teamwork
Simulation experiences often involve teamwork scenarios, teaching students the importance of clear communication and collaboration in healthcare settings. For instance, simulation exercises may involve students working together to manage a simulated medical crisis, delegating responsibilities, and coordinating care efficiently. This training fosters effective teamwork and communication, crucial for managing complex healthcare situations.
Increased Confidence and Competence
Repetitive practice in a controlled, supportive environment allows students to gain confidence and competence in their clinical skills. Nursing students who regularly engage in simulation exercises report feeling significantly more prepared and less anxious when transitioning into clinical placements or professional roles. The simulation ensures that students feel ready to handle real patient interactions, enhancing their overall effectiveness as healthcare providers.
The Future of Simulation in Nursing Education
As healthcare continues to evolve, simulation technologies will undoubtedly become even more sophisticated and integral to nursing education. Emerging trends include increased integration of augmented reality (AR), tele-simulation for remote training, and artificial intelligence (AI) to provide adaptive learning experiences tailored to individual student needs.
Healthcare simulation is a powerful educational tool that significantly enhances nursing students’ practical skills, clinical judgment, and confidence. The thoughtful integration of high-fidelity mannequins, virtual reality, and task trainers ensures students are exceptionally well-prepared for successful careers in nursing. Through simulation, education transforms into experience, shaping the next generation of highly skilled, compassionate healthcare providers.
At CNI College, we remain committed to staying at the forefront of these developments, ensuring our students benefit from the latest technological advancements in healthcare simulation. By investing in state-of-the-art simulation equipment and continuously enhancing our simulation curriculum, we prepare our nursing students not just to meet current healthcare demands but to thrive and lead in the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare.